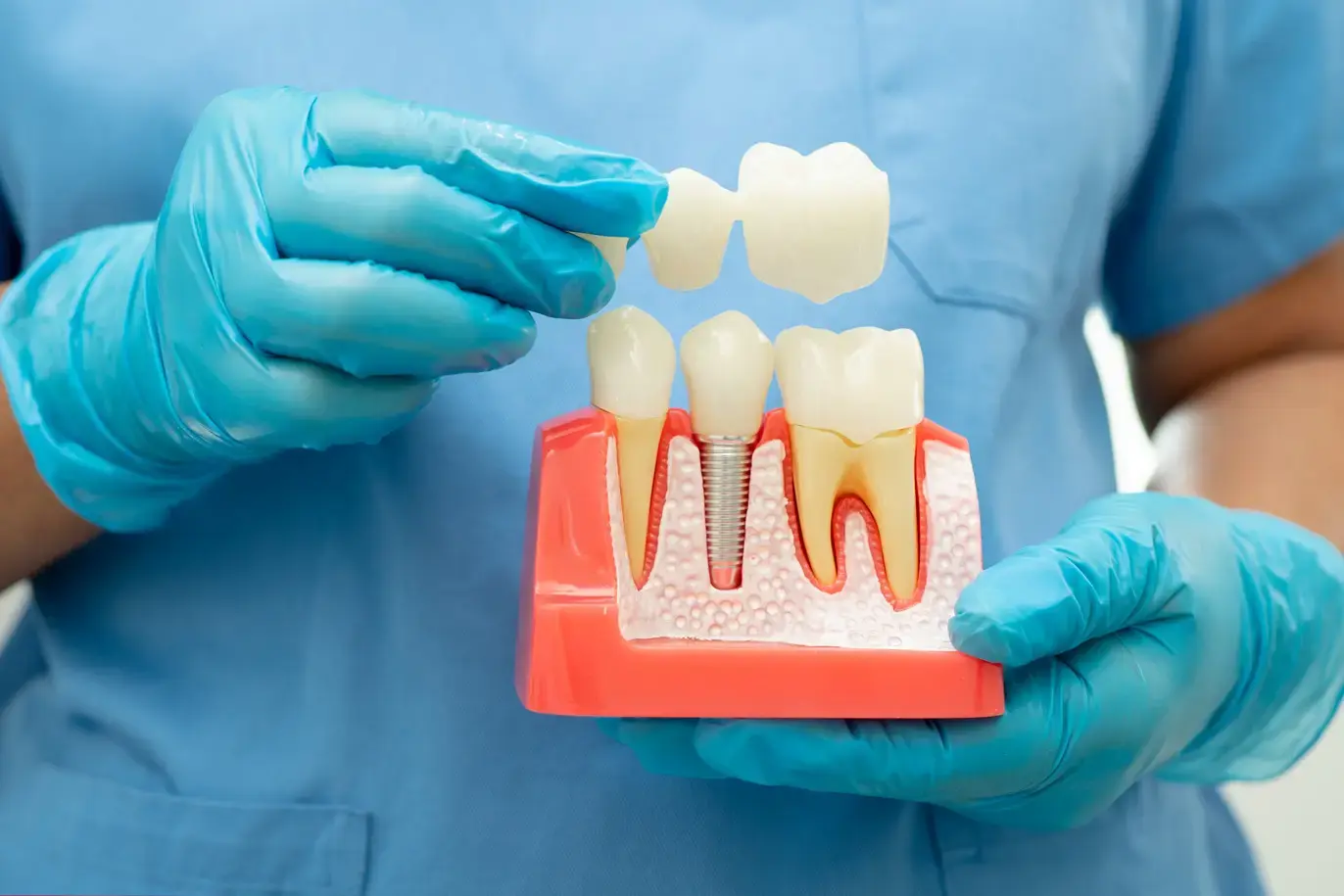
Tooth Loss
Tooth loss is a condition in which there is loss of one or more teeth. This impacts dental health, alignment, balance of biting forces, and aesthetics as well as speech. To avoid tooth loss, it is very important to understand the cause of tooth loss. Tooth loss sometimes may also be referred to as edentulism.
Why Understanding Tooth Loss Matters
Losing a tooth isn't just about appearance — it can lead to difficulties in chewing, jawbone deterioration, and even impact your confidence and communication. Recognizing the signs early can help with timely prevention.
Types of Tooth Loss
Partial Edentulism: There is absence of one or more teeth in both jaws while the other teeth in the jaw are intact.
Total Edentulism: In this there is complete loss of teeth in one or both arches of jaw.
Common Causes of Tooth Loss
Tooth loss may result from tooth decay, any form of dental trauma, genetic predisposition, accidental avulsion, etc.
Other Contributing Risk Factors
-
Gum disease (periodontitis)
-
Smoking or tobacco use
-
Poor oral hygiene
-
Chronic medical conditions like diabetes
Prevention and Treatment
Using protective gear during sports or other activities, practicing proper dental hygiene, and maintaining good oral hygiene practices are preventive ways to avoid tooth loss.
Treatment Options for Tooth Loss
Treatment modalities depend upon the location, oral and general health of the patient, as well as his/her age.
For kids who lose teeth too soon, space maintainers, dental bridges, dentures, and dental implants are available options.
When to See a Dentist
If you notice persistent pain, loose teeth, or gum swelling, it's essential to seek a dental evaluation early. Early diagnosis can prevent further tooth loss and preserve your smile.
Long-Term Effects of Untreated Tooth Loss
-
Jawbone resorption
-
Shifting of remaining teeth
-
Bite misalignment
-
Speech changes
-
Facial structure changes
You May Also Like
These Related Stories
Have A Bump On Your Gums Causes And Treatments
.png)